
One retrospective cohort study on 11 eyes treated with methotrexate injections showed improvement in inflammatory reactions and tumor cell infiltration in all treated eyes. Specifically, intravitreal injections of dexamethasone, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor, and methotrexate are being examined. Īs traditional systemic treatment approaches may have limited penetrance into the vitreous, intravitreal injections have recently been explored as adjunctive treatments. Leukopheresis and allogeneic bone marrow transplant are also sometimes necessary depending on severity and disease progression. If chemotherapy fails to diminish intraocular leukemic infiltrates, direct radiation therapy is recommended. CML on the other hand, is initially treated with busulfan or hydroxyurea.
ALL treatment consists of various combinations of vincristine, prednisone, and L-asparagine, while AML is treated with Daunorubicin, cytarabine, and thioguanine. Chemotherapy is the primary treatment modality and depends on the type of leukemia, as well as the phase of progression. While there is no direct curative treatment for leukemic retinopathy, such approaches can help diminish the systemic disease. Patients should be treated for the underlying leukemia by chemotherapy, immunotherapy or radiotherapy.

Secondary to clusters of cells occluding retinal arterioles, not usually associated with hematological parameters

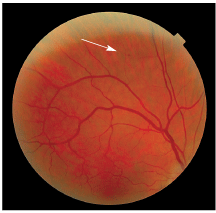
Retinal hemorrhages at all levels – especially in the posterior pole, and extension to the vitreousįigure 4: Fundus photo of right eye showing cotton wool spots around the disc Image Courtesy: Rajan Eye Care Hospital, Chennai, India History of treatment such as chemotherapyġ.ĝilated and tortuous veins – early manifestations due to hematological disturbances Ģ.History of any other systemic illnesses.History of leukemia or any other malignancies- acute/chronic.Prolonged leukocytosis increased number of circulating platelets -> Increased whole blood viscosity -> Reduced blood flow and vascular stagnation -> Peripheral capillary dropout and microaneurysm formation -> Proliferative retinopathy Ĝhemotherapy related high doses of glucocorticoids can cause ocular hypertension, cataracts, diplopia, and various other disorders. ĜNS involvement through infiltration of the optic nerve, causing papilledema due to high intracranial pressure, and cranial nerve palsies. Hematological abnormalities such as anemia and thrombocytopenia, leading to intraretinal hemorrhages, white-centered retinal hemorrhages, cotton-wool spots, macular hemorrhages, subhyaloid hemorrhages, and vitreous hemorrhages. Primary or Direct due to infiltration of the orbit, iris, choroid, optic nerve, and other tissues by leukemic tumour cells Ocular complications of leukemia can either be :ġ. Retinal manifestations are usually due to indirect complications of leukemia especially due to hematological abnormalities (Figure 1).Figure 1: Fundus of the right eye of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia showing retinal hemorrhages suggestive of leukemic retinopathy Image Courtesy: Rajan Eye Care Hospital, Chennai, India


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
